| Title | Maximizing on-farm groundwater recharge with surface reservoir releases: a planning approach and case study in California, USA |
|---|---|
| Resource Author(s) |
|
| Year of Publication | 2019 |
| Link to Report/Website | springer.com |
| Document Upload | Gailey-et-al.-2019-Maximizing-on-farm-groundwater-recharge-with-surfa.pdf |
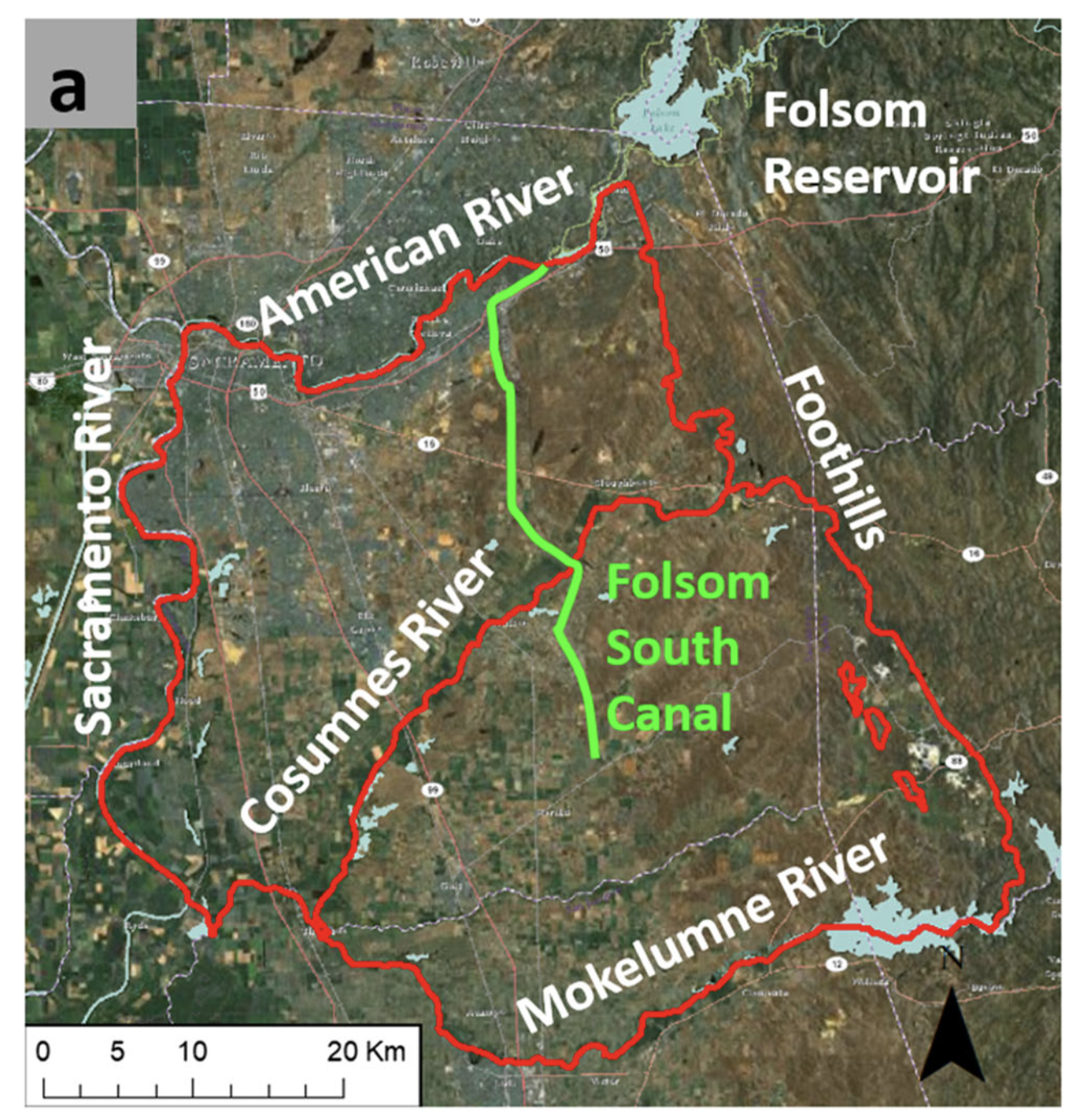
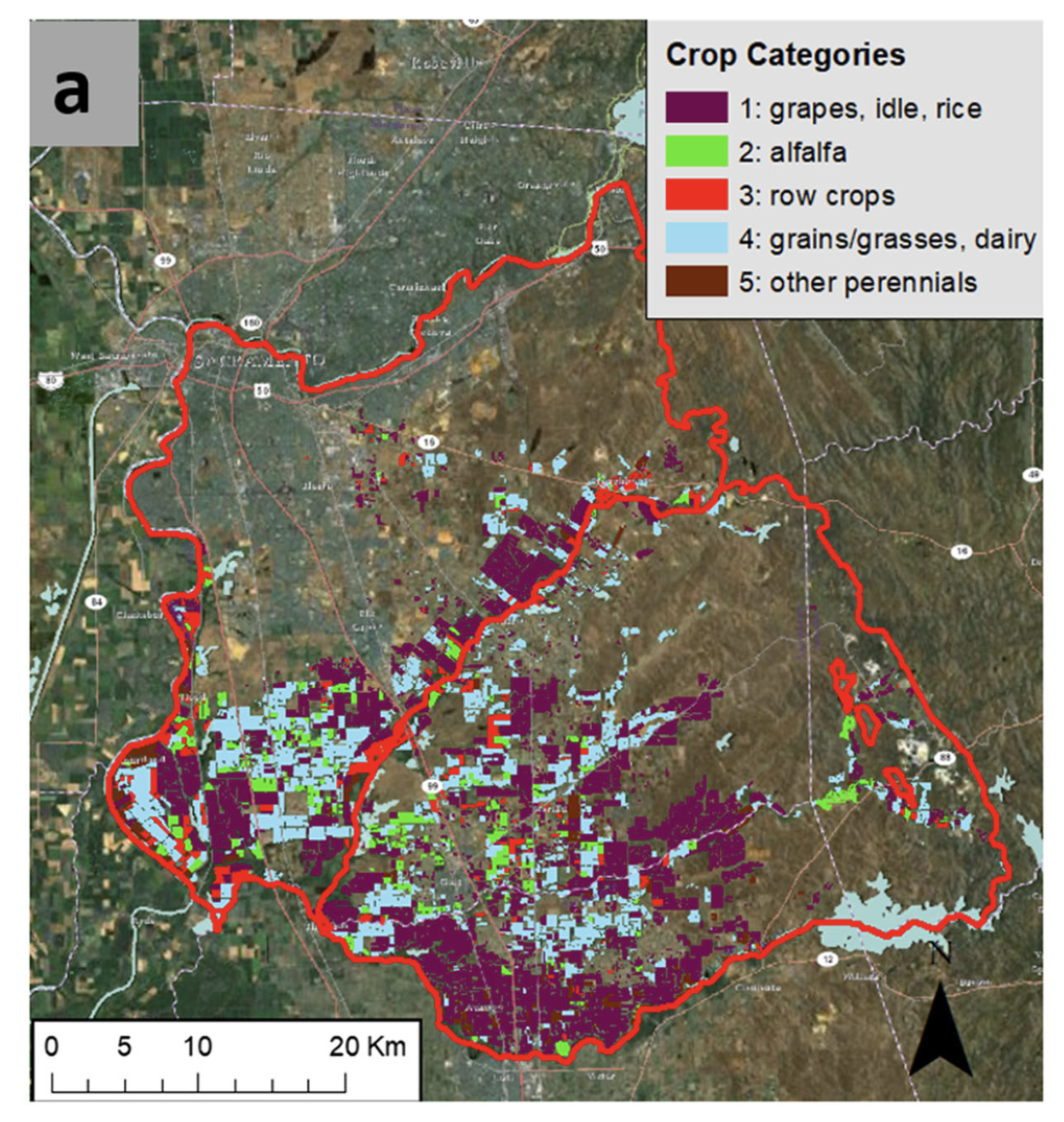
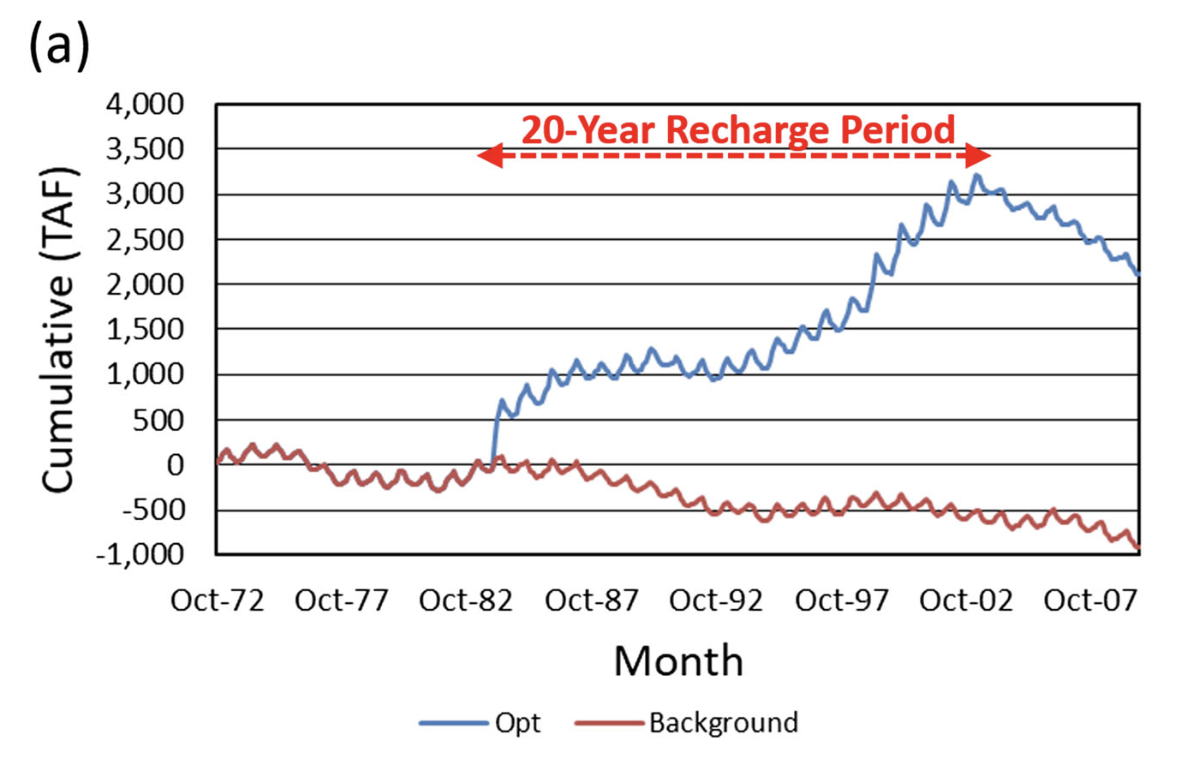
| Full Description | A hydro-economic approach for planning on-farm managed aquifer recharge is developed and demonstrated for two contiguous sub-basins in California’s Central Valley, USA (American-Cosumnes basin). The amount and timing of water potentially available for recharge is based on a reoperation study for a nearby surface-water reservoir. Privately owned cropland is intermittently used for recharge with payments to landowners that compensate for perceived risks to crop health and productivity. Using all cropland in the study area would have recharged approximately 4.8 km3 (3,900 thousand acre-feet) over the 20-year analysis period. Limits to recharge effectiveness are expected from (1) temporal variability in recharge water availability, (2) variations in infiltration rate and few high-infiltration recharge sites in the study area, and (3) recharged water escaping from the study area groundwater system to surface water and adjacent sub-basins. Depending on crop tolerance to ponding depth, these limitations might be reduced by (1) raising berm heights on higher-infiltration-rate croplands and (2) creating dedicated recharge facilities over high-infiltration-rate sites. |
 | |
| Resource Host Organization, Partner Organizations (Optional) |
|
| Topic Area(s) |
|
 | |
 | |
Privacy Overview
This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
Strictly Necessary Cookie should be enabled at all times so that we can save your preferences for cookie settings.
If you disable this cookie, we will not be able to save your preferences. This means that every time you visit this website you will need to enable or disable cookies again.
